In this blog🤌,
we will explore the DOM, its importance in web development, and how it enables dynamic interaction with web pages. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, this blog will help you understand the fundamental concepts of the DOM and how it works.
What is the DOM?🤔
The Document Object Model (DOM) defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated.
The Document Object Model, or DOM, is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It represents the structure of a web page as objects that can be manipulated using JavaScript or other scripting languages. Simply put, the DOM acts as a bridge between web pages and scripts, allowing us to interact with and modify the content, structure, and styles of a web page dynamically.
Understanding the DOM Tree🌳🫠
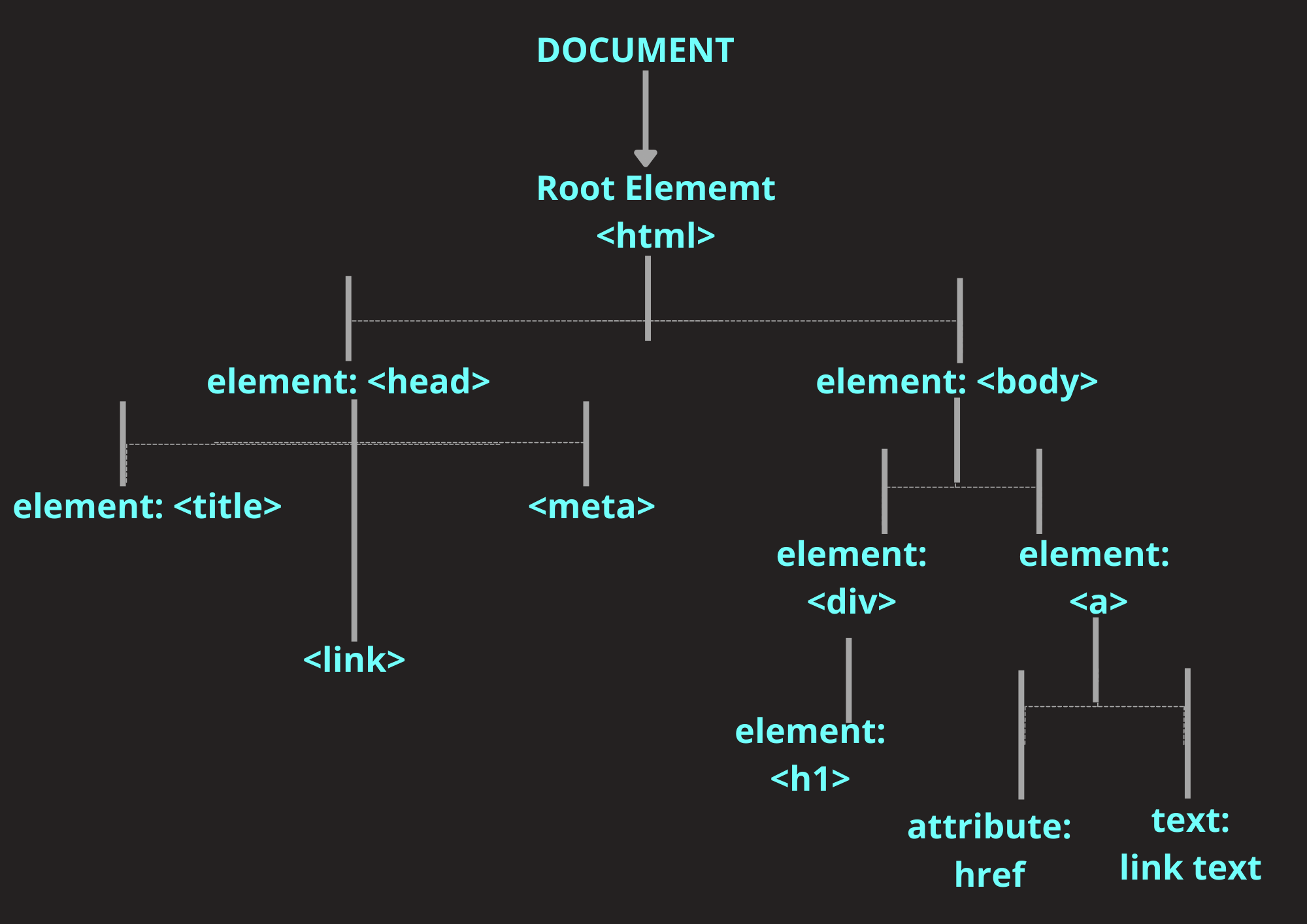
To better grasp the concept of the DOM, let's visualize it as a tree-like structure. Each HTML element, attribute, and text node in a web page becomes a node in the DOM tree. The relationships between these nodes represent the hierarchical structure of the HTML document.
Here's an example of a simple HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Interactive Blog</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, DOM!</h1>
<p>Welcome to our interactive blog on the DOM.</p>
</body>
</html>
The DOM representation of this document would look like this:
- Document
- html
- head
- title
- #text
- body
- h1
- #text
- p
- #text
As per the Document Object Model (DOM), each HTML tag, including the text within the tags, is treated as an individual object. All the data within these tags are stored and managed as objects. Consequently, everything in HTML is organized in a structured manner, forming a data structure tree known as the DOM tree.
This tree arrangement allows for a logical representation of the relationships and hierarchies between elements, facilitating efficient manipulation and interaction with the content of web pages.
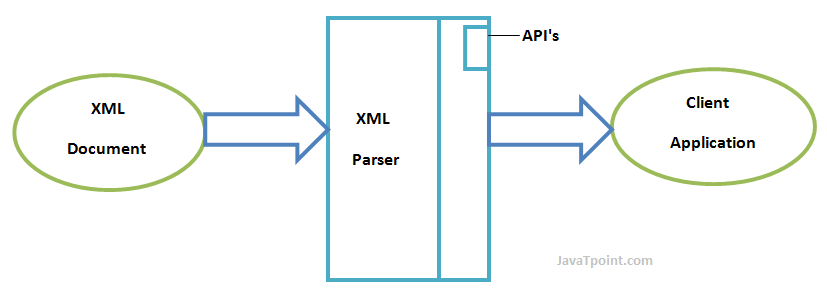
The DOM Parser🕵️♀️
A DOM parser is a software component that parses HTML or XML documents and creates a Document Object Model (DOM) tree, representing the document's structure. This tree allows programs to interact with and manipulate the content and elements of the document efficiently.
How to Access DOM Elements😚
- By ID:
Suppose there is an element with the ID 'header':
var headerElement = document.getElementById('header');
• By TagName:
Suppose there are multiple 'div' elements in the document:
var divElements = document.getElementsByTagName('div');
• By ClassName:
Suppose there are elements with the class 'highlight':
var highlightElements = document.getElementsByClassName('highlight');
• By CSS Selectors:
Suppose you want to select an element with the class 'btn':
var buttonElement = document.querySelector('.btn');
• By querySelectorAll():
Suppose you want to select all elements with the class 'link':
var linkElements = document.querySelectorAll('.link');
• parentNode:
Suppose you have an element called 'child' and you want to access its parent node:
var childElement = document.getElementById('child');
var parentElement = childElement.parentNode;
• firstElementChild:
Suppose there is a 'ul' element with 'li' elements inside, and you want to access the first 'li' element:
var ulElement = document.querySelector('ul');
var firstLiElement = ulElement.firstElementChild;
• lastElementChild:
Suppose there is a 'ul' element with 'li' elements inside, and you want to access the last 'li' element:
var ulElement = document.querySelector('ul');
var lastLiElement = ulElement.lastElementChild;
These methods allow you to find specific elements within the DOM and perform various operations on them using JavaScript.
The DOM is extensively utilized by developers in JavaScript for creating dynamic web pages. However, let's examine the benefits and drawbacks of utilizing the DOM:
Advantages of DOM:
Provides a structured representation of web documents, allowing easy access and manipulation of content using programming languages like JavaScript.
Enables dynamic and interactive web pages, enhancing user experience and interactivity.
Disadvantages of DOM:
Large DOM trees can slow down web page performance and increase memory consumption.
Direct manipulation of the DOM can lead to potential security vulnerabilities if not handled carefully.
Conclusion 🙇♀️
To conclude, the DOM is a tree made up of all elements in an HTML document. Moreover, It is a set of Javascript objects with certain properties and characteristics.
Congratulations! You've now learned the basics of the DOM and how to manipulate it using JavaScript.
Remember that these examples are just the tip of the iceberg. There's so much more you can do with the DOM, like modifying styles, handling events, and creating interactive web experiences.
I hope you enjoyed this interactive blog on the DOM.
Happy coding 😫🧨
If you have any questions or want to share your experiences, leave a comment below❤️🔥
